Advancements In Oil Fume Monitoring Sensors
Release time:2025-12-19
Visits:1
Oil fumes stand as a critical imperative across industrial landscapes, presenting multifaceted hazards to occupational health and environmental integrity. Acknowledging the paramount importance of robust emissions monitoring, technological advancements in oil fume monitoring sensors have evolved into an indispensable cornerstone of proactive safety governance and regulatory adherence. This article delves into the latest innovations in sensor technology, their specialized industrial applications, and their transformative influence on air quality management frameworks.
In sectors spanning advanced manufacturing, automotive engineering, metal fabrication, and thermal processing, oil fumes are inherent byproducts of high-temperature operations—including machining, heat treatment, lubricant degradation, and metalworking processes. These fumes comprise complex matrices of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs), and respirable particulate matter (PM₂.₅/PM₁₀), substances linked to chronic respiratory disorders, systemic toxicity, and long-term carcinogenic risks with prolonged exposure. Consequently, real-time, precise monitoring of such emissions is not merely a regulatory obligation but a fundamental commitment to worker protection and environmental stewardship.
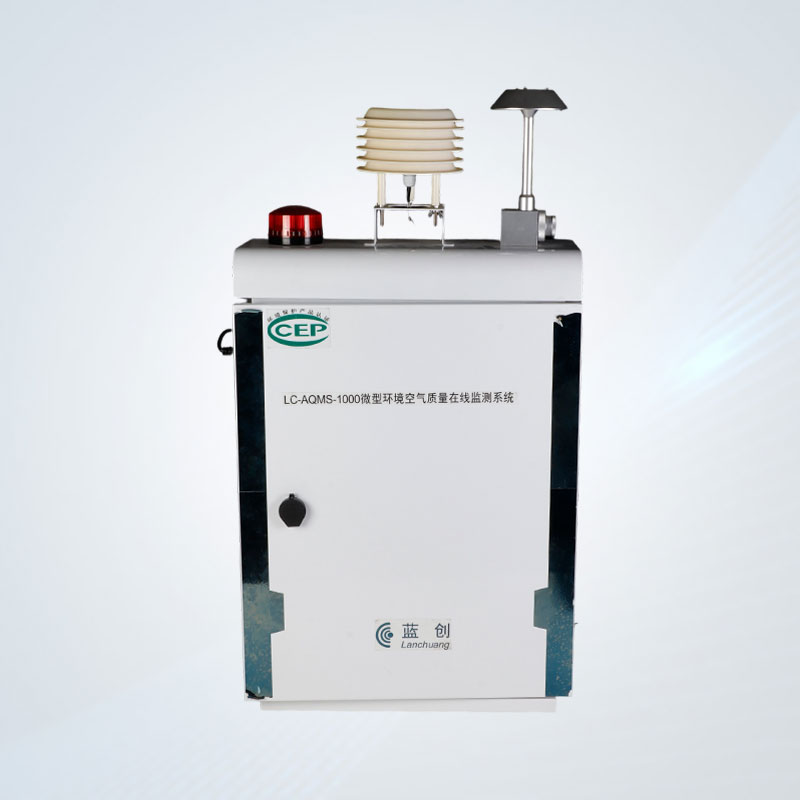

Recent advancements in oil fume
monitoring sensors have centered on three core pillars: precision engineering, sensitivity enhancement, and intelligent data analytics. Contemporary sensors integrate state-of-the-art sensing modalities—such as photoionization detectors (PID), metal oxide semiconductors (MOS), and laser-induced fluorescence (LIF) modules—with machine learning algorithms, enabling selective detection and quantitative analysis of target pollutants at ppb (parts per billion) concentration levels. This granularity ensures that even trace quantities of hazardous compounds, often undetectable by conventional sensors, are identified with exceptional accuracy, facilitating timely intervention to mitigate exposure risks.
A defining trend in sensor development is the integration of oil fume monitoring capabilities into holistic air quality sensing ecosystems. By combining oil fume detection with the monitoring of complementary pollutants (e.g., nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, and carbon monoxide), these integrated systems deliver a comprehensive assessment of industrial air quality. This interconnected approach empowers organizations to implement data-driven Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) strategies, aligning operational practices with global regulatory frameworks such as the U.S. EPA’s Clean Air Act, the EU’s Industrial Emissions Directive (IED), and ISO 14001 environmental management standards.
VOC detection remains a focal point of innovation, given the class’s role as a primary contributor to both occupational health hazards and atmospheric pollution. Advanced sensors now feature enhanced cross-sensitivity rejection, minimizing interference from non-target gases and ensuring reliable VOC quantification even in complex industrial environments with variable emission profiles—such as automotive assembly lines or metalworking facilities where process parameters fluctuate dynamically.
Perhaps the most transformative advancement is the shift toward real-time data processing and autonomous control integration. Modern oil fume sensors leverage edge computing and IoT (Internet of Things) connectivity to transmit continuous, high-resolution data to centralized EHS management platforms. This real-time visibility enables stakeholders to make agile, data-informed decisions, reducing latency between pollutant detection and response. Furthermore, built-in automation capabilities allow sensors to trigger preconfigured control measures—including adaptive ventilation systems, process parameter adjustments, or emergency shutdown protocols—without human intervention, significantly enhancing workplace safety and operational resilience.
The evolution of oil fume monitoring sensors has redefined industrial air quality management, transitioning from reactive compliance to proactive risk mitigation. By delivering precise, actionable data, these technologies enable organizations to safeguard worker health, minimize environmental footprints, and demonstrate regulatory compliance with greater efficiency. Beyond immediate operational benefits, they also support the broader adoption of sustainable industrial practices, aligning with global initiatives to reduce hazardous emissions and advance circular economy principles.
In conclusion, the ongoing advancement of oil fume monitoring sensors is indispensable to fostering safer, more sustainable industrial environments. As technology progresses—with anticipated innovations in miniaturization, energy efficiency, and multi-pollutant detection—these sensors will become increasingly integral to EHS management strategies. By embracing these cutting-edge solutions, industries can not only meet evolving regulatory requirements but also uphold a steadfast commitment to protecting human health and preserving the environment for future generations.