Ammonia Nitrogen Water Quality Automatic Analyzer
Release time:2025-12-22
Visits:1
Water quality monitoring constitutes a foundational pillar of public health protection and ecological preservation, with ammonia nitrogen (NH₃-N) emerging as a critical indicative parameter for assessing aquatic ecosystem integrity and potable water safety. Elevated NH₃-N concentrations typically signal anthropogenic contamination or ecological imbalance, posing severe risks to aquatic biota (via acute toxicity and eutrophication) and human health (through the formation of disinfection byproducts in drinking water systems). The ammonia nitrogen water quality automatic analyzer has thus evolved into an indispensable tool for continuous, high-precision water quality surveillance, enabling data-driven environmental management and regulatory compliance.
Ammonia nitrogen—a compound formed by the combination of nitrogen and hydrogen—accumulates in water bodies through multiple pathways, including agricultural non-point source pollution (e.g., fertilizer leaching, livestock manure runoff), industrial discharges (e.g., wastewater from chemical synthesis, food processing, and coal-fired power plants), municipal sewage effluents, and natural biogeochemical processes (e.g., organic matter decomposition in anoxic environments). In excessive quantities, NH₃-N triggers eutrophication—a cascade effect characterized by algal blooms, dissolved oxygen (DO) depletion, and the formation of hypoxic "dead zones"—which disrupts aquatic food webs and renders water unfit for consumption, recreation, or industrial use. Consequently, rigorous and continuous NH₃-N monitoring is not only a regulatory mandate but also a proactive measure to safeguard ecological resilience and public health.
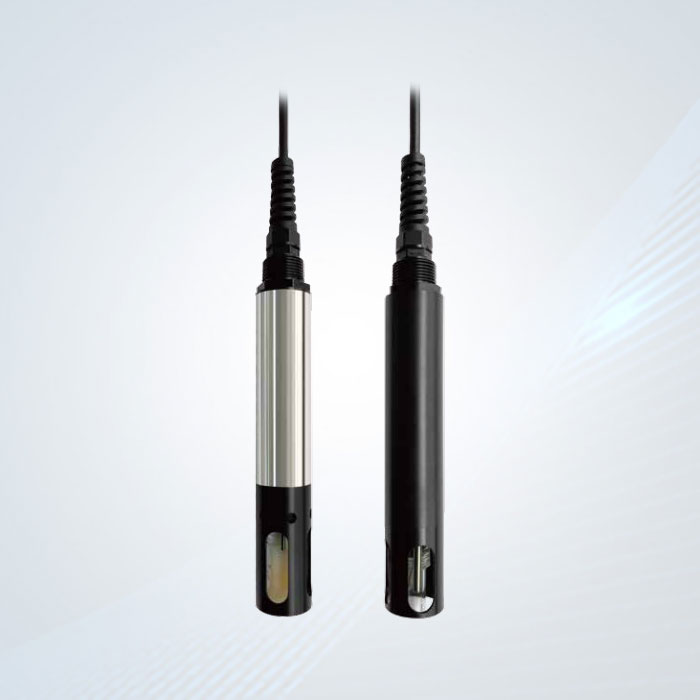

Modern ammonia nitrogen
water quality automatic analyzers are engineered to deliver uninterrupted real-time monitoring functionality, providing granular, time-stamped data on NH₃-N concentrations. This capability enables the rapid detection of concentration fluctuations and potential contamination events (e.g., accidental industrial spills, agricultural runoff surges), allowing environmental managers, wastewater operators, and regulatory bodies to implement swift corrective actions—such as adjusting treatment processes, isolating contaminated water sources, or initiating pollution investigations—thereby minimizing ecological and public health impacts.
A core advantage of these analyzers lies in their superior accuracy, precision, and trace-level detection capabilities. Equipped with advanced sensing technologies (e.g., ion-selective electrodes (ISEs), spectrophotometric detection modules, or gas-sensitive semiconductor sensors) and automated calibration systems (including zero-point and span calibration cycles), they eliminate the inherent limitations of manual testing methods—such as human error, sampling bias, and delayed result turnaround. These technical enhancements ensure reliable quantification of NH₃-N concentrations across a broad dynamic range (typically 0.01–100 mg/L), even in complex water matrices (e.g., high-turbidity wastewater, brackish water, or industrial effluents with high organic load).
Contemporary designs prioritize user-centric functionality without compromising technical performance. Intuitive human-machine interfaces (HMIs), featuring touchscreen displays, customizable data dashboards, and remote access capabilities (via IoT connectivity), ensure operability for personnel across varying technical skill levels. Additionally, built-in data logging, storage, and transmission modules enable seamless integration with centralized water quality management platforms, facilitating long-term trend analysis, compliance reporting, and cross-parameter correlation (e.g., linking NH₃-N levels to pH, temperature, and dissolved oxygen).
The applications of ammonia nitrogen automatic analyzers span multiple critical sectors:
- Environmental Monitoring: Deployed in rivers, lakes, reservoirs, and coastal waters, these analyzers enable regulatory agencies to track NH₃-N trends, assess the effectiveness of pollution control measures, and enforce compliance with water quality standards (e.g., the U.S. EPA’s Clean Water Act, the EU’s Water Framework Directive, and China’s GB 3838-2002 Surface Water Environmental Quality Standard).
- Wastewater Treatment Facilities: As a key component of process control systems, they monitor NH₃-N concentrations in influents, biological treatment stages, and final effluents. This ensures optimal operation of nitrification/denitrification processes, guarantees effluent compliance with discharge limits, and prevents the release of nutrient-rich wastewater that exacerbates eutrophication.
- Industrial Compliance: Industries generating nitrogen-containing wastewater (e.g., chemical manufacturing, food and beverage processing, aquaculture, and agriculture) rely on these analyzers to maintain adherence to regulatory discharge permits. Proactive monitoring minimizes the risk of non-compliance penalties, reputational damage, and ecological harm.
Beyond regulatory compliance, ammonia nitrogen automatic analyzers deliver substantial operational and environmental value. By automating data collection and analysis, they reduce labor costs associated with manual sampling, transport, and laboratory testing, while eliminating the latency of off-site analysis. The availability of real-time data empowers stakeholders to optimize treatment processes, reduce resource consumption (e.g., energy, chemicals), and implement proactive pollution mitigation strategies—aligning with global sustainability goals (e.g., UN Sustainable Development Goal 6: Clean Water and Sanitation).
While the upfront capital investment for automatic analyzers may exceed that of manual testing equipment, the long-term return on investment is compelling. Operational efficiencies (reduced labor, lower chemical usage, minimized downtime), risk mitigation (avoidance of non-compliance fines, liability for environmental damage), and ecological co-benefits (preserved aquatic ecosystems, sustained water resource availability) collectively outweigh initial costs.
In conclusion, the ammonia nitrogen water quality automatic analyzer represents an indispensable cornerstone of modern water resource management. Its ability to deliver continuous, accurate, and actionable NH₃-N data empowers organizations to safeguard water quality, comply with regulatory requirements, and advance environmental sustainability. As sensing technologies evolve—with anticipated improvements in miniaturization, energy efficiency, and multi-parameter integration—these analyzers will further solidify their role as critical tools for addressing global water challenges, ensuring the long-term viability of aquatic ecosystems and public health.